Investing in infrastructure can help achieve sustainable development goals (SDGs), provide equal opportunities to citizens through, for instance, accessible roads and transportation and create more resilient and greener infrastructures. Public investment had been weak globally, despite massive infrastructure needs.
Public investment is expensive and for most countries the needed resources are daunting, particularly amid high debt and little fiscal space. Countries need strong infrastructure governance institutions that ensure that scarce resources are spent well both to build new infrastructure and maintain existing assets.
The IMF’s Public Investment Management Assessment (PIMA) is a tool that assesses the strengths and weaknesses of a country’s public investment management system and proposes reforms to improve the quality of public investment by strengthening infrastructure governance. PIMAs have been conducted in more than 80 countries around the world (see chart below).
On the basis of the PIMAs conducted up to July 2022, the IMF has published the PIMA Handbook.
The Handbook is intended to be useful for country authorities, IMF staff, staff of other development banks and agencies, and anyone who is interested in understanding how public investment management systems are designed in different countries and how they work in practice.
The Handbook provides an overview of the PIMA framework and a detailed description of each of the 15 PIMA institutions (or practices) and 45 sub-dimensions involved in the key stages of the public investment cycle (planning, allocation and implementation), as well as three cross-cutting institutions (the legal framework, IT systems, and capacity development).
A valuable aspect of the Handbook is its presentation of good practice examples based on countries’ experience from around the world, and the differentiation between institutions as defined in laws and regulations compared to their effectiveness on the ground.
Short PIMA videos were developed to summarize the framework and the 15 PIMA Institutions.
Distribution of PIMAs around the World, 2015-22
(Average scores on Institutional Design and Effectiveness by region)
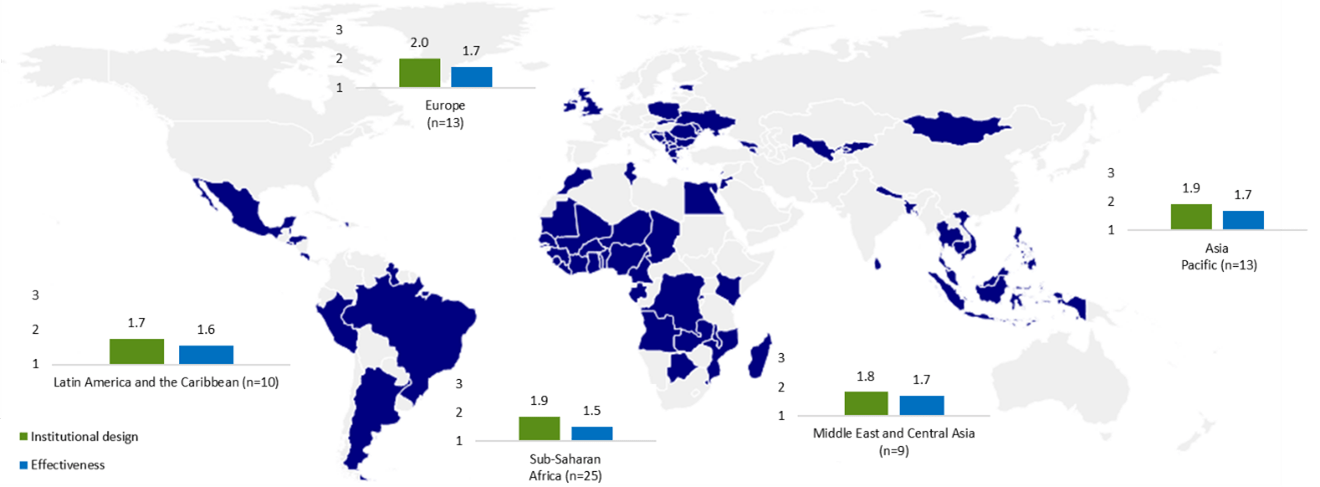
Source: IMF staff calculations based on PIMA reports.
Note: Shaded countries are those that have conducted PIMAs. Institutional design and effectiveness are measured on a scale of 1 to 3, with best practice being a score of 3. PIMA = Public Investment Management Assessment.






